LiDAR technology, often associated with modern applications like autonomous driving, has a rich history that dates back almost 60 years. Far from being a recent innovation, LiDAR has undergone significant development, with its origins rooted in terrain mapping, environmental monitoring, and various other applications. Here’s a look at how the history of LiDAR unfolded.
The Beginnings of LiDAR Technology
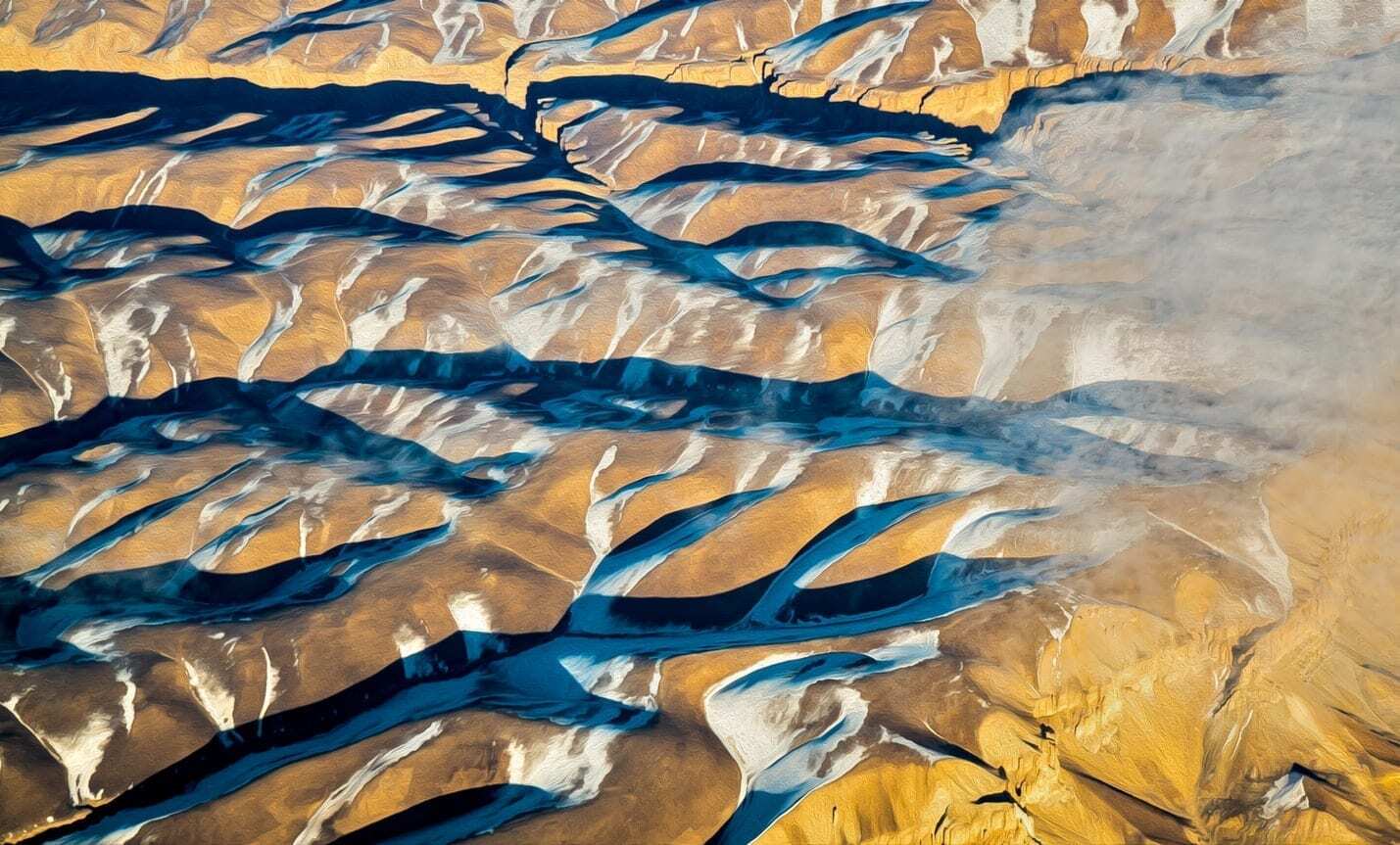
The story of LiDAR begins in the 1960s when the first systems were developed for use in terrain mapping, particularly in the fields of aeronautics and aerospace. In the 1970s, the technology expanded to remote sensing, with airborne sensors used to map topographic features like forests, ice sheets, oceans, and the atmosphere. One surprising application occurred under NASA’s Apollo 15 mission, where LiDAR was employed for surface mapping on the moon.

Growth and Challenges in the 1980s
LiDAR development advanced slowly at first, particularly due to the lack of commercial GPS systems, which were crucial for deploying aerial sensors. It wasn’t until the 1980s that GPS solutions and satellite communications enabled the widespread use of aerial photogrammetry, making LiDAR more accessible for mapping large areas. The laser light’s ability to detect tiny objects such as aerosols and cloud particles proved essential for both airborne and terrestrial mapping, laying the foundation for future applications.
LiDAR’s Commercialization in the 1990s
By the mid-1990s, the first commercial LiDAR systems were created, offering 2,000 to 25,000 pulses per second for topographic mapping. These systems quickly demonstrated the potential of LiDAR for high-resolution mapping, confirming its position as a critical technology for geospatial applications. The ability to combine LiDAR with photogrammetry allowed for better feature data collection and flight planning, cementing LiDAR as a powerful tool for environmental monitoring.
The Rise of LiDAR Technology
LiDAR’s ability to offer fast, precise, and non-inferential 3D mapping made it a game-changer for environmental monitoring and land surveys. Unlike traditional photogrammetric methods, LiDAR could provide a more accurate representation of the terrain, even in complex environments like forests. Over time, as prices stabilized, LiDAR technology became more affordable and widely used for 3D mapping, further solidifying its role in scientific research and commercial applications.
LiDAR Today: Applications and Advancements
It lies in the nature of LiDAR evolution to bring along new ways and applications for science and industry to integrate 3D sensing. With each new field opening up, subsequent usage scenarios can be derived and developed. Consequentially, this is how the proliferation of laser-based sensing technology was and is enhanced.
LiDARs for commercial and non-commercial use – such as in military or research implementations – constantly evolved during the last two decades. Today, up to 2 million data points per second can be generated within 5 mm accuracy. LiDAR sensing entered a wide range of different fields in which it is still in use up till today, such as:
- Glacial Monitoring: Tracking ice mass changes and studying climate change.
- Ground Movement Measurement: Monitoring tectonic activity in vulnerable regions.
- Shoreline Change: Assessing the impact of rising sea levels on coastlines.
- Landslide Risk Assessment: Identifying areas prone to landslides.
- Urban Planning: Designing infrastructure and assessing environmental impacts.
- Traffic Management: Optimizing traffic flow and improving mobility in cities.
- Crowd Analytics: Enhancing safety and planning for large gatherings.
- Security: Improving perimeter monitoring and intrusion detection systems.
Conclusion
The history of LiDAR shows how a technology initially used for specialized scientific and military purposes has expanded into a diverse array of industries. From its early days in terrain mapping to its current applications in environmental monitoring, traffic management, and security, LiDAR’s evolution continues to drive advancements in 3D sensing technology. As LiDAR systems become even more accurate and efficient, the possibilities for its use will only continue to grow, reaffirming its place in the technological landscape.








